Types of Down Syndrome
Are There Different Types of Down Syndrome?
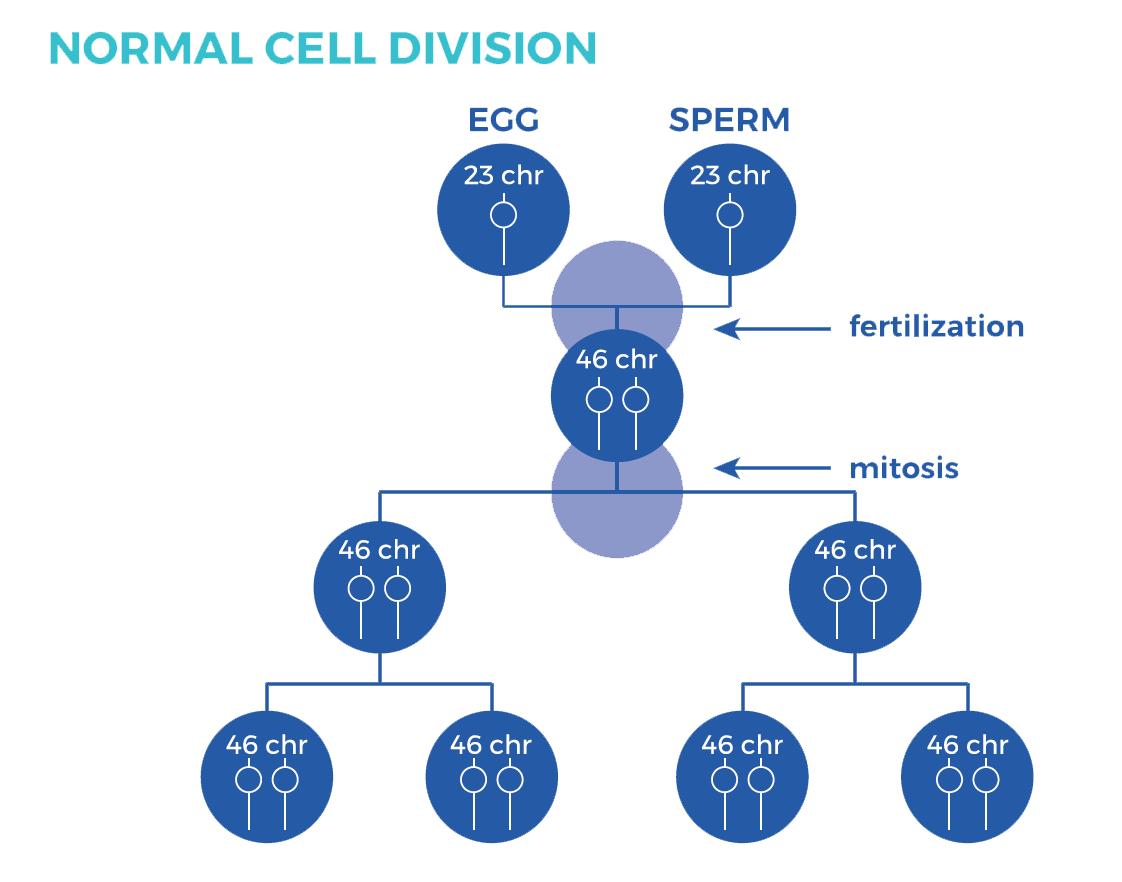
There are three types of Down syndrome: Trisomy 21 (nondisjunction), Mosaicism, and Translocation. Below is a chart that outlines the cell division process of regular cells.
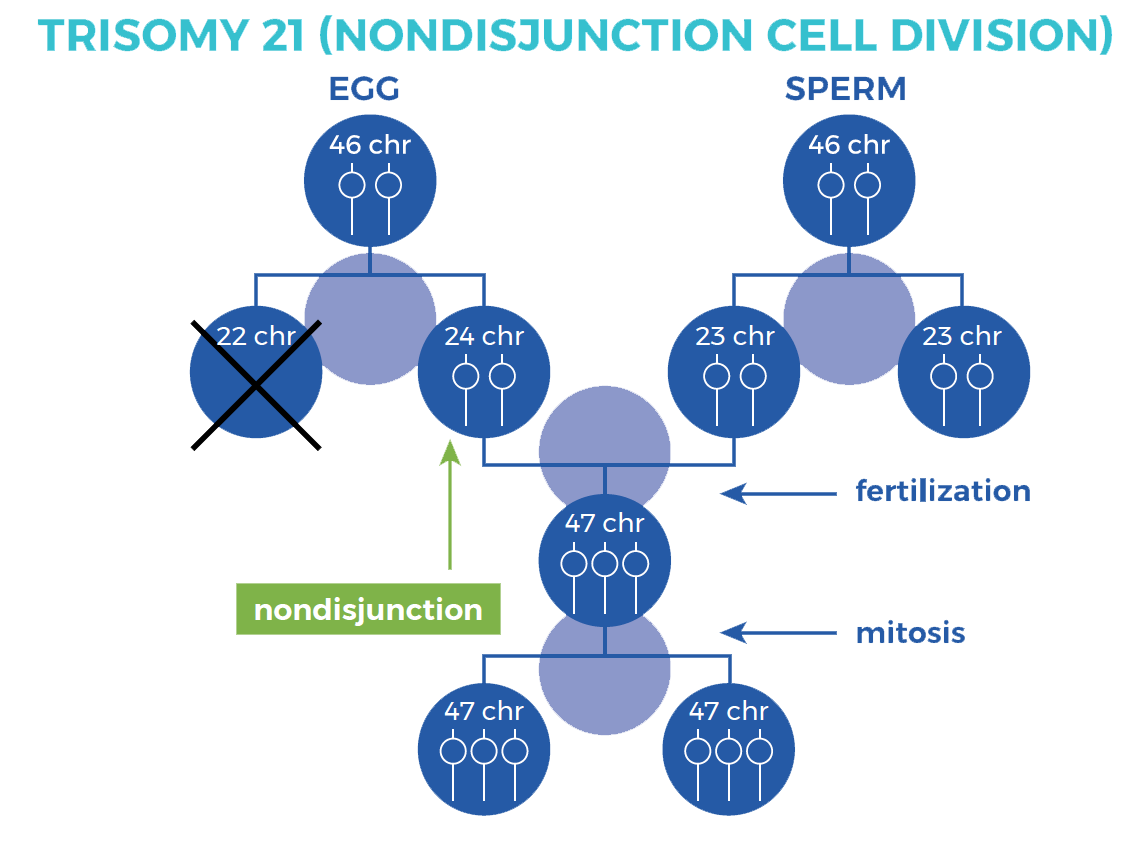
Trisomy 21 (Nondisjunction)
Down syndrome is usually caused by an error in cell division called “nondisjunction.” Nondisjunction results in an embryo with three copies of chromosome 21 instead of the usual two. Prior to or at conception, a pair of 21st chromosomes in either the sperm or the egg fails to separate.
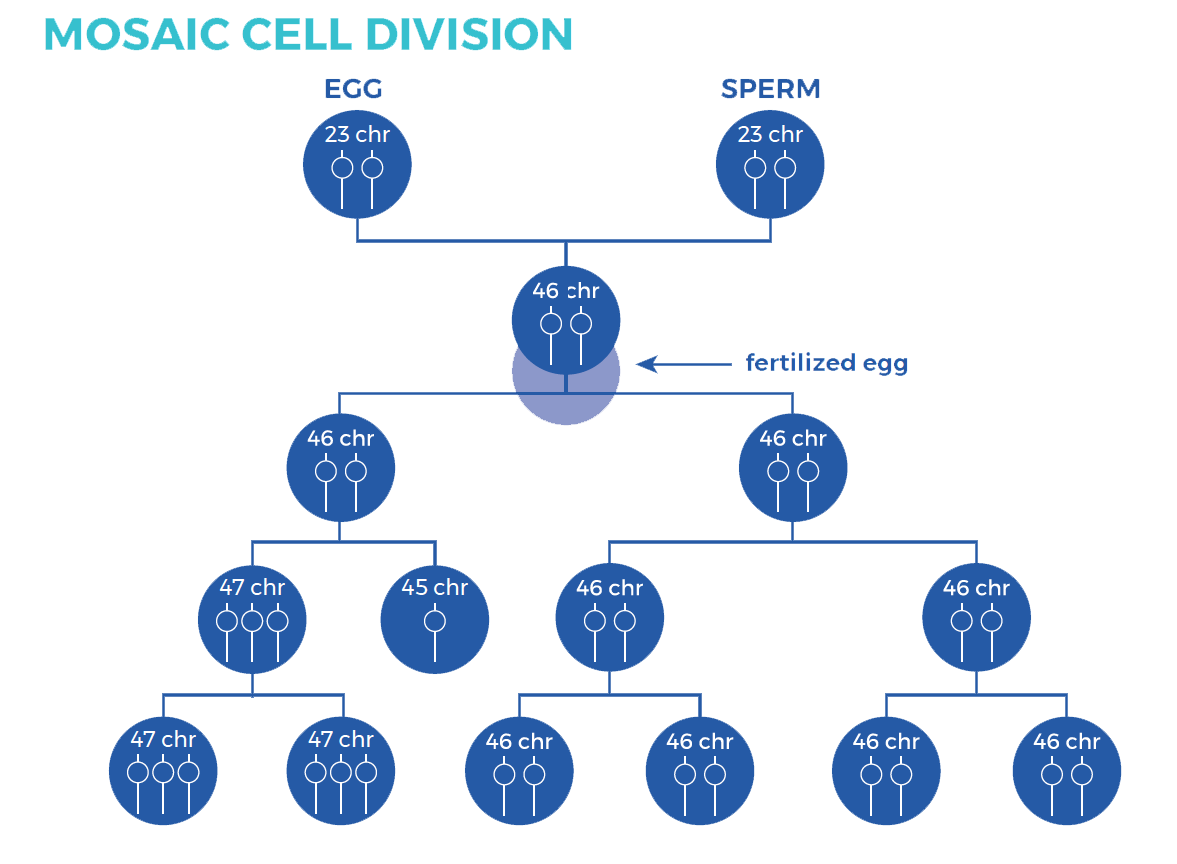
Mosaicism
Mosaicism (or mosaic Down syndrome) exists when there are a mixture of two types of cells, some containing the usual 46 chromosomes and some containing 47. Those cells with 47 chromosomes contain an extra chromosome 21.
Translocation
In translocation, which accounts for about 4% of cases of Down syndrome, the total number of chromosomes in the cells remains 46. However, an additional full or partial copy of chromosome 21 attaches to another chromosome, usually chromosome 14. The presence of the extra full or partial chromosome 21 causes the characteristics of Down syndrome.

